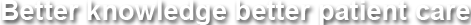Mr Willis, a 45 old company executive presents with chronic symptoms of heartburn. An endoscopy showed:
What is the diagnosis?
Barrett’s oesophagus
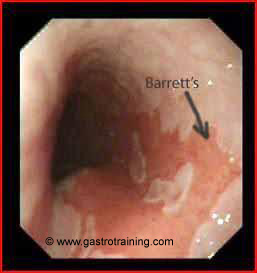
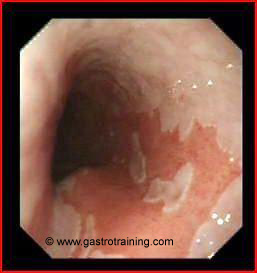
What is Barrett’s oesophagus?
Barrett’s oesophagus” (more appropriately referred to as columnar-lined oesophagus [CLO]) is an oesophagus in which any portion of the normal squamous lining has been replaced by a metaplastic columnar epithelium which is visible macroscopically.
Discuss the measurement of the length of Barrett’s oesophagus?
Studies show that there is inter- and intraobserver reliability in measuring Barrett’s length. Accurate measurements of Barrett’s oesophagus length are important in clinical follow-up as well as in studies of therapeutic intervention in Barrett’s oesophagus.
To correctly measure the length of Barrett’s oesophagus, it is important to identify some key landmarks at endoscopy:
Gastro oesophageal junction is defined endoscopically as the level of the most proximal gastric fold. When the squamo-columnar junction is proximal to the gastroesophageal junction (i.e. the most proximal gastric fold), there is a columnar-lined segment or Barrett’s oesophagus.
The squamo-columnar junction is usually visible as the pale squamous epithelium merges into redder columnar mucosa. If the squamo-columnar and gastroesophageal junction coincide, the entire oesophagus is lined with squamous mucosa.
Discuss the role of endoscopy in patients with chronic heartburn?
British society of Gastroenterology (BSG) does not recommend endoscopic screening of patients with chronic heartburn to detect CLO.
Discuss the biopsy protocol for Barrett’s oesophagus?
Quadrantic biopsies should be taken every 2cm in the columnar segment together with biopsies of any visible lesion.
Discuss surveillance visa a vis the length of Barrett’s oesophagus?
The length of the CLO segment has been linked to an increased risk of developing dysplasia or carcinoma development but the relationship seems weak. Consequently, modifying clinical management according to CLO segment length is not warranted at present.
Thus, BSG recommends surveillance (if appropriate) every 2 years irrespective of the length of Barrett’s oesophagus.
What is the role of PPI in Barrett’s oesophagus?
Longitudinal cohort studies of patients with Barrett’s oesophagus suggest that use of PPI may be associated with reduced risk of dysplasia. It may be that chronic inflammation associated with GORD promotes carcinogenesis. However, PPI’s has not been shown to reduce the length or progression of Barrett’s, or to reduce acid exposure adequately in up to 30-40% of patients despite high dose PPI.
In clinical practice, most patients are advised long term PI based on the premise that chronic acid exposure leads to Barrett’s oesophagus.
What is the role of antireflux surgery in Barrett’s oesophagus?
There is insufficient evidence to suggest it reduces incidence of adenocarcinoma.
Discuss chemoprevention in Barrett’s?
The majority of adenocarcinoma is thought to arise from Barrett’s. Experimental and epidemiological data suggest use of NSAID’s may reduce risk of cancer in Barrett’s patients. ASPECT trial, due to report in 2011, is looking at the long-term chemoprevention effect of esomeprazole with or without aspirin.
Further reading