Hartmann’s operation
Discuss Hartmann’s operation?
- Performed by Hartmann for the first time in 1921. He envisaged the operation to be definitive with the patient having a permanent terminal colostomy.
- Controversy exists over the choice of surgery for emergency left colonic surgery. Hartmann’s procedure is generally the preferred choice in case of peritonitis. A single stage resection and anastomosis may be done in the other cases like obstructed left colon cancer.
- Hartmann’s operation is preferred in left colonic emergencies particularly in presence of peritonitis because
- Concerns that peritoneal contamination adjacent to an anastomosis could increase the risk of anastomotic leak
- Resection and primary anastomosis takes significantly longer in a sick patient
- Improvements in surgical and radiological intervention techniques and progress in the management of peritoneal sepsis have led to an increasing interest in colonic resection with primary anastomosis (PA).
What does Hartmann’s operation entails?
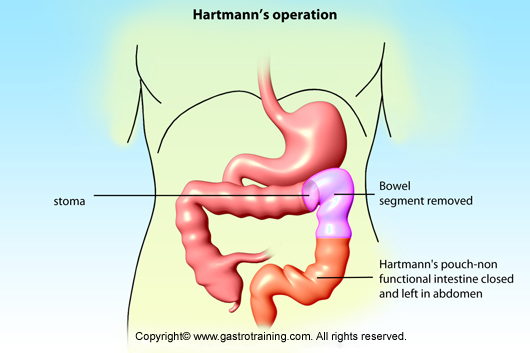
- Hartmann’s operation refers to the resection of a diseased portion of the left colon, with the proximal end of the colon brought out as a colostomy and the distal recto-sigmoid stump being closed by suture in the pelvis.
- Rectal stump can also be left open as stoma in the LIF (mucous fistula).
- This operation is commonly done following sigmoid colectomy for perforation, when the proximal descending colon after mobilizing by dissecting it from splenic flexure is brought out in left iliac fossa as end colostomy. The patient will have a colostomy bag in the left iliac fossa.
Discuss re anastomosis?
- The colostomy can be left as permanent or the resected bowel can be re-anastomosed in a subsequent operation.
- One-third of the patients fail to undergo subsequent restoration of bowel continuity. Even using stapling devices to facilitate the reversal of a Hartmann’s procedure, it can be technically difficult due to small bowel adhesions in the pelvis.
- Re anastomosis should only be attempted at least 3 months after the primary surgery.
Hartmann’s Operation