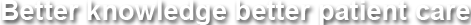Balloon PEGs
The module covers:
- Two different types of Balloon PEG- Button PEG (Low profile balloon gastrostomy tube) and replacement balloon PEG
- When to use which one and how
Low profile balloon gastrostomy tube (also called button PEG)
- This is for the individual who is ambulatory and feels the long PEG tube is socially inconvenient (not to be confused with Replacement balloon PEG which also has got a balloon as a retaining device)
- Once the tract is formed – remove the old PEG
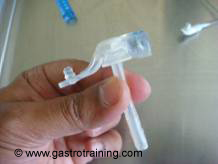
Picture1: The measuring device - Use the measuring device to measure the length of the tract
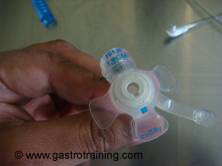
Picture2: 16 French 3cm Corflo cuBBy PEG- low profile gastrostomy tube - Choose your balloon PEG – length and the French gauge- and get customized low profile balloon PEG for that particular patient
- Accurate length is important as there is no sliding outer retaining device (in contrast to the Replacement balloon gastrostomy PEG) – so if the tube is longer than necessary it can bob up and down and stoma will leak.
- Introduce the lubricated tip of the Low profile balloon gastrostomy tube gently into the tract
- Inflate the balloon with the required amount of water

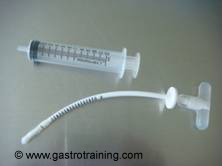
Picture3: The extension tube to be attached just before feed - Before the feed- the attachment tube needs to be fixed – the blue mark on the attachment tube needs to be aligned with the blue mark on the button PEG and turned by 90 degrees
- Once feed is over the extension tube is turned in the opposite direction and removed
- Because of the extension tube needs to be repeatedly connected and disconnected -button PEG tends to wear out and needs replacement on a regular basis
Replacement balloon gastrostomy tube
- This tube is placed if an old PEG has fallen/pulled out and there is a well formed and matured tract
- Disadvantage over endoscopically inserted PEG is that it’s life is much shorter compared to the former.
- Once the PEG falls out -the tract may close as early as 4 hours -so quick replacement (with balloon PEG or Foley’s catheter) is needed
- Clean the stoma
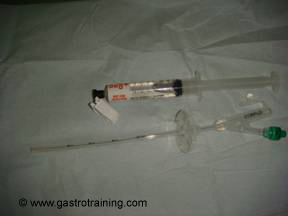
Picture4: The replacement balloon gastrostomy tube (not to be confused with button PEG or low profile device which also has got a balloon as a retaining device) - Insert the lubricated balloon PEG into the stoma gently and it should pass freely without much resistance
- Inflate the balloon with water – 5-6ml
- Pull the tube out until the balloon stops it- slide the outer fixation bumper snugly to the skin
- Attach the extension tube with the Y connector- one takes bladder wash syringe and the other- Luer lock syringe
- After care- the patient or the carer to check the water amount in the balloon and top up as and when necessary
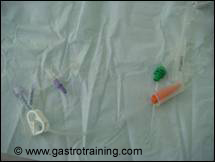
Picture5: The extension tube with the Y connector
Here are the links for button PEG and replacement balloon PEG insertion video’s respectively:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hSv4FOwZ9kQ&feature=related
Acknowledgement/Bibliography:
- Guidelines for enteral feeding in adult hospital patients : BSG 2003
- Novotny NM et al. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy buttons in children: superior to tubes. J Pediatr Surg. 2009;44(6):1193-6
- Heiser M et al. Balloon-type versus non-balloon-type replacement percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: which is better? Gastroenterol Nurs. 2001 Mar-Apr;24(2):58-63
- Product guide of the respective companies- Merck Serono and Flocare