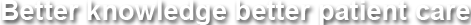Abdominal vasculature
Discuss the abdominal aorta?
The abdominal aorta begins at the aortic opening in the diaphragm (at about T12) and descends anterior to the vertebral bodies and ends at L4 by dividing into the right and left common iliac arteries.
Each common iliac artery divides into the external and internal iliac arteries. The external iliac artery passes posterior to the inguinal ligament to become the femoral artery. The external iliac artery gives off the inferior epigastric and deep circumflex iliac arteries. The internal iliac artery supplies most of the pelvis via parietal and visceral branches.
The parietal branches of the internal iliac artery include the iliolumbar, lateral sacral, obturator, superior and inferior gluteal, and internal pudendal arteries. The branches of the internal pudendal artery include the inferior rectal artery and vessels that supply the scrotum (or labia), perineum, bulb of the penis (or vestibule), and urethra.
The visceral branches of the internal iliac artery includes the umbilical and superior and inferior vesical arteries, the uterine artery (or the artery of the ductus deferens), and the vaginal and middle rectal arteries.
Discuss the branches of abdominal aorta?
Parietal branches
- Paired lumbar arteries- supply the muscles of the back and provide spinal branches.
- Median sacral artery- unpaired artery arising near the bifurcation and descends to the coccygeal body.
Visceral branches
Paired middle suprarenal, renal gives rise to inferior suprarenal arteries), and gonadal (ovarian/testicular) arteries.
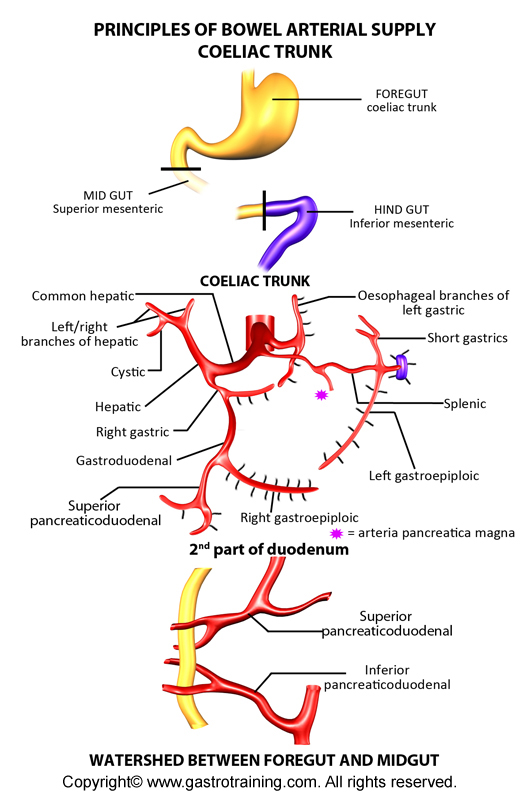
Coeliac trunk
It is the artery to the caudal part of the foregut, i.e., as far as D2. It divides into
- Left gastric- it runs along the lesser curve and anastomoses with the right gastric artery
- Splenic artery- it runs to the left along the upper border of pancreas. It gives off pancreatic branches, left gastroepiploic artery (runs along greater curve), short gastric arteries and splenic branches.
- Common hepatic artery- divides into the hepatic artery proper, the right gastric artery, and the gastroduodenal artery. The hepatic artery proper divides into right and left branches, the former of which gives off the highly variable cystic artery. The gastroduodenal artery gives off the posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery, and divides into the anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal and right gastroepiploic arteries.
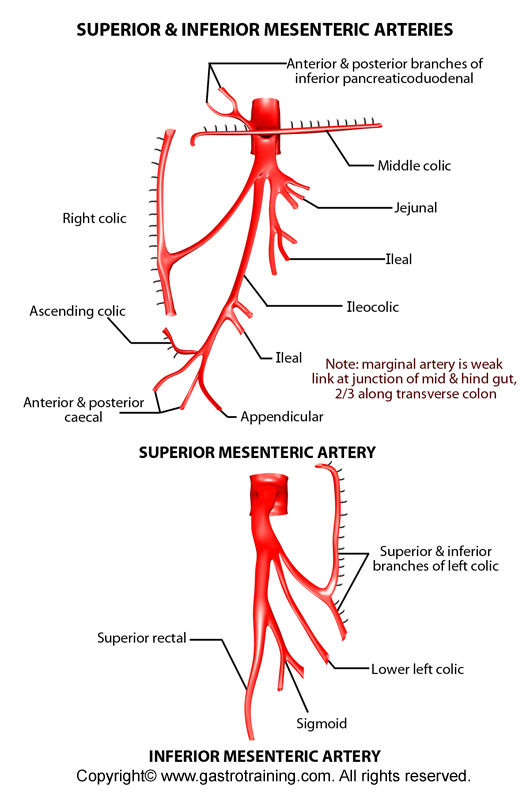
Superior mesenteric artery
It supplies the midgut, i.e., from D2 to the proximal 2/3rd of the transverse colon. It arises from the front of the aorta inferior to the origin of the coeliac trunk. Its branches include:
- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery (it divides into anterior and posterior components)
- Jejunal and ileal arteries to the small intestine.
- Ileocolic artery
- Right colic artery
- Middle colic artery
Inferior mesenteric artery
It supplies the hindgut, i.e., from the distal third of the transverse colon to the rectum. It arises from the aorta a little superior to its bifurcation. Its branches are
- Left colic
- Sigmoid arteries
- Superior rectal artery- it is the continuation of the inferior mesenteric artery